A visa is an official travel document issued by a country’s government that grants permission to enter, stay, or leave its territory for a specific purpose and duration. Typically attached to a traveler’s passport, this document serves as proof that the individual has been authorized to visit the destination country — whether for tourism, work, study, or business.
The type of visa you need depends on several factors, including the purpose of your travel, the length of your stay, and your nationality. Some nations have visa-free agreements that allow citizens to visit without a visa, while others maintain strict entry requirements for all foreign visitors. Common categories include tourist, work, student, and transit visas.
However, it’s essential to understand that holding a visa does not guarantee entry. Final approval rests with immigration officers at the border, who can deny access based on their country’s entry policies. Moreover, visa rules and application procedures can vary significantly between countries and may change at any time. Therefore, always verify the latest requirements with the official embassy or consulate before making travel plans.
A Brief History of Travel Visas.
The term “visa” originates from the Modern Latin phrase “charta visa,” meaning “paper that has been seen” or “approved document.” Over time, it came to represent the official authorization that permits a person to enter or stay in a foreign country.
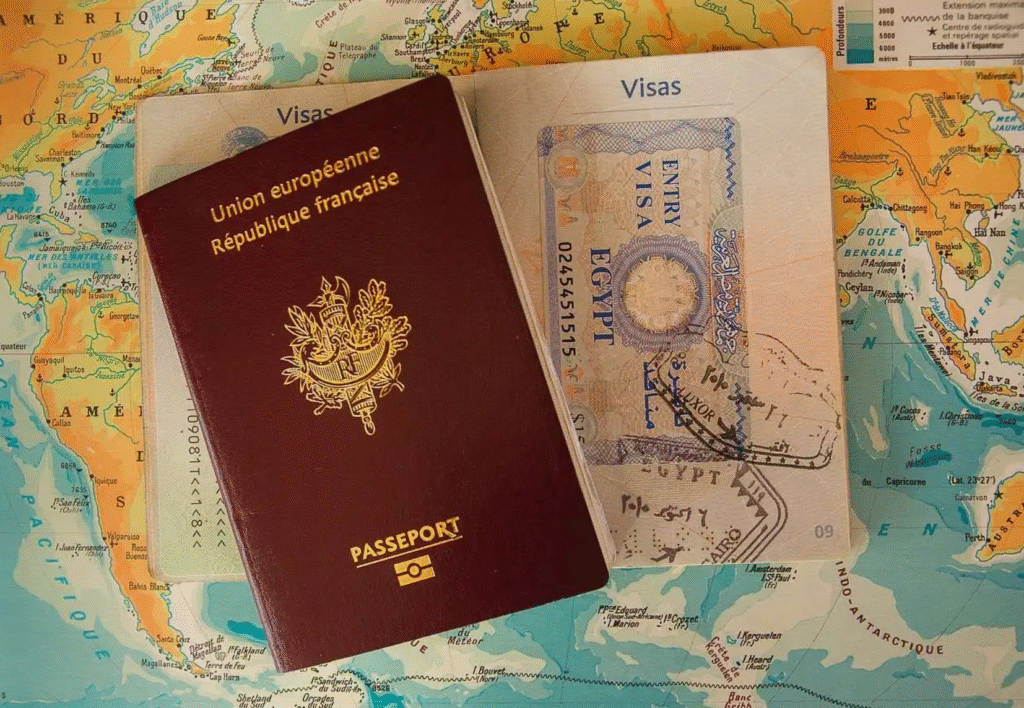
Sometimes, a visa is issued as a separate document rather than being stamped or affixed to your passport. This is common with electronic visas (e-visas), which travelers are often required to print out and carry during their trip.
Visa Type By Purpose.
Some of the most common types of travel visas include the following categories:
Tourist Visa.
A tourist visa is a short-term travel permit issued to individuals visiting a foreign country for leisure, vacation, or sightseeing purposes. It allows travelers to explore and enjoy the destination but does not permit any paid employment.
Typically, tourist visas are valid for up to 90 days (three months), though the exact duration can vary depending on the country’s immigration policies. Travelers must leave the country before their visa expires or apply for an extension if permitted by local laws.

Transportation Visa.
A transit visa allows travelers to pass through a country on their way to a third destination. It is designed for passengers who make short stops or layovers in another country before continuing their journey.
For example, if you hold an Indian passport and are traveling to Canada with a stopover in a Schengen country, you’ll need to obtain a Schengen transit visa.
Typically, a transit visa is valid for 24 to 96 hours, though some countries may issue it for up to ten days or even two weeks, depending on their immigration policies. Importantly, you must apply for a transit visa before traveling, as airports generally do not issue these visas on arrival.
Medical Visa.
To qualify for a medical visa, applicants must submit a medical certificate or a doctor’s report confirming their health condition and the need for treatment abroad. In addition, travelers must provide proof of arrangements with a recognized hospital or specialist in the destination country who will perform the required medical procedures.
Working Holiday Visa.
A working holiday visa is a short-term permit that combines the benefits of a tourist visa and a work visa. This visa allows travelers to explore a foreign country for leisure while working temporarily to fund their trip.
Most countries impose restrictions on the type of work allowed and the number of hours you can work while on a working holiday visa. Typically, these visas are valid for one to two years, and most travelers can apply only once, except in countries like Australia, which may allow multiple applications.
Eligibility for a working holiday visa usually requires applicants to be between 18 and 30 years old, though age limits may vary by country.
Student Visas.
A student visa is a travel permit issued for educational purposes that allows international students to study in a foreign country for the duration of their academic program. The validity of a student visa typically ranges from 1 to 4 years, depending on the length of the course or program.
While holding a student visa, working abroad is generally restricted, unless the host country explicitly permits students to take up part-time or on-campus employment. Always check the work allowances and regulations of your destination country before planning any employment.
Work Visa.
If you plan to take up employment in a foreign country, you must apply for a work visa. This type of visa is typically issued for long-term employment, often up to four years, though the exact duration depends on your employment contract and the host country’s immigration rules.
A work visa can serve as a pathway to permanent residency, allowing employees to eventually apply for a long-term stay or citizenship, depending on local laws and regulations.
Family Reunification Visa.
A family reunification visa is granted to individuals whose spouse or partner is living and working abroad. This visa allows you to join your family as a temporary or permanent resident in the country where your partner resides.
In addition to spouses, minor children are often eligible for inclusion under the same family visa, allowing the entire family to live legally together in the host country.
Investment Visa.
An investment visa enables individuals to gain residency in a foreign country by making a substantial financial investment. This investment can take various forms, such as starting a business, investing in local companies, or purchasing real estate, depending on the host country’s regulations.
Many countries offer investment visas as a pathway to long-term residency or citizenship, making them an attractive option for entrepreneurs, investors, and property buyers looking to relocate internationally.
Official Visa.
An official visa is issued to individuals representing their country in diplomatic or governmental activities abroad. The most common type is a diplomatic visa, but some countries also provide service visas or courtesy visas for government officials traveling on official business.
Official visas allow holders to perform diplomatic duties, attend international meetings, or engage in government-related work while in the host country, often with certain privileges and immunities under international law.
Refugee Or Asylum Visa.
A refugee visa or asylum visa is issued to individuals who face persecution in their home country due to religion, race, nationality, political opinion, or membership in a particular social group. This type of visa allows individuals to seek protection and legal residence in a foreign country.
Each country has its own procedures and requirements for granting refugee or asylum status, ensuring that those in need of protection can safely reside while their claims are being evaluated.
Digital Nomad Visa.
A digital nomad visa allows individuals to live in a foreign country while working remotely for a company or clients based elsewhere. Eligibility criteria vary by country, but generally, applicants must demonstrate that they can perform their job remotely and earn a sustainable income while residing abroad.
This type of visa is designed for remote workers, freelancers, and location-independent professionals who wish to experience life in another country without relocating their employer or business.
Retirement Visa.
A retirement visa allows foreign nationals to live in another country after reaching retirement age. Typically issued as a residence permit, this visa is designed for individuals who wish to spend their retirement abroad.
Applicants are usually required to demonstrate sufficient financial resources to support themselves during their stay. Some countries may also have additional requirements, such as health insurance or proof of accommodation, to ensure retirees can live comfortably and securely.
Hajj Visa.
A Hajj visa is a special permit issued to individuals who wish to undertake the Islamic pilgrimage to Mecca. For example, Saudi Arabia issues Hajj visas to Muslims from around the world who plan to perform the holy pilgrimage during the designated Hajj season.
This visa is typically time-limited and intended solely for religious travel, ensuring that pilgrims can participate in Hajj rituals legally and safely.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a visa?
A visa is an official document issued by a country that permits you to enter, stay, or leave that country for a specific purpose and duration.
Why do I need a visa to travel?
Many countries require visas to control immigration, ensure security, and regulate foreign visitors. The need for a visa depends on your citizenship and destination country.
What are the different types of visas?
Common visa types include tourist visas, work visas, student visas, transit visas, family reunification visas, investment visas, medical visas, and digital nomad visas. Each type serves a specific purpose.
Can I work in a foreign country with a tourist visa?
No. Tourist visas are strictly for leisure or sightseeing, and working on a tourist visa is usually prohibited. You must obtain a work visa to work legally abroad.
Do all countries require visas?
No. Some countries have visa-free agreements that allow citizens of certain nations to enter without a visa for a limited period. Always check your destination’s entry requirements.
What is an e-visa or electronic visa?
An e-visa is a digital visa issued online, which may need to be printed or carried digitally. It is often used instead of a traditional passport stamp or sticker.
Does having a visa guarantee entry into a country?
No. A visa permits you to travel to the border, but immigration officers have the final authority to allow or deny entry.
Conclusion
A visa is a crucial travel document that allows individuals to enter, stay, and sometimes work or study in a foreign country. Understanding the different types of visas, such as tourist, work, student, transit, and investment visas, helps travelers choose the right option for their journey.